
- Blog
- 2025 LLM Paradigm Shifts: Six Big Changes
2025 LLM Paradigm Shifts: Six Big Changes
Large Language Models crossed several conceptual thresholds in 2025. Beyond raw scale, the field discovered new training stages, new app layers, and new ways to interact with AI. Here are six paradigm shifts that, taken together, reshaped how we build, evaluate, and use LLMs.
Table of Contents
- Reinforcement Learning from Verifiable Rewards (RLVR)
- Ghosts vs. Animals / Jagged Intelligence
- Cursor and the new layer of LLM apps
- Claude Code: AI that lives on your computer
- Vibe coding
- Nano banana and the LLM GUI
- FAQ
- Conclusion
Reinforcement Learning from Verifiable Rewards (RLVR)
What changed
From ~2020 to ~2024, the production recipe was stable: Pretraining → Supervised Finetuning (SFT) → RLHF. In 2025, RLVR became the fourth major stage. By optimizing against objective, automatically verifiable rewards (think math/code puzzles), models learned to produce longer, structured reasoning traces and to iteratively backtrack—behaviors that look like “reasoning” to humans. OpenAI’s o1 previewed this, but o3 marked the inflection.
Why it matters
- Longer, objective optimization: Unlike relatively short SFT/RLHF phases, RLVR can run much longer because rewards are hard to game.
- Capability per dollar: Teams diverted compute from pretraining to extended RLVR runs, yielding similar model sizes but noticeably smarter behavior.
- A new scaling knob: You can trade test-time compute for capability by increasing “thinking time” (longer traces, more search), giving a practical way to dial performance.
Practical guidance
- Treat verifiable environments as capability engines; curate task suites that truly capture your domain’s invariants.
- Separate “reward model design” from “trace policy design” and track both; subtle reward shaping induces qualitatively different strategies.
- Budget for evaluation drift: longer traces change failure modes; design evals that stress both correctness and robustness under increased thinking time.
Ghosts vs. Animals / Jagged Intelligence
The shape of model intelligence
LLMs aren’t “growing animals.” They’re “summoned ghosts” optimized under very different pressures: imitation of human text, verifiable puzzle rewards, and human preferences. As RLVR expands in verifiable domains, we see sharp capability spikes near those pockets—leading to jagged performance: at once a brilliant polymath and a gullible grade-schooler.
Benchmarks in 2025
Benchmarks are often verifiable environments; unsurprisingly, they become targets for RLVR and synthetic data. Labs inevitably benchmaxx—constructing training environments adjacent to benchmark pockets, then growing jaggies to envelop them. The result: incredible scores that don’t necessarily generalize.
What to measure next
- Non-verifiable reasoning: tasks where intermediate steps are ambiguous or require open-ended synthesis.
- Distribution shifts: deliberate, staged shifts beyond benchmark neighborhoods.
- Robustness to adversarial instruction: jailbreak resilience is now table stakes for deployment.
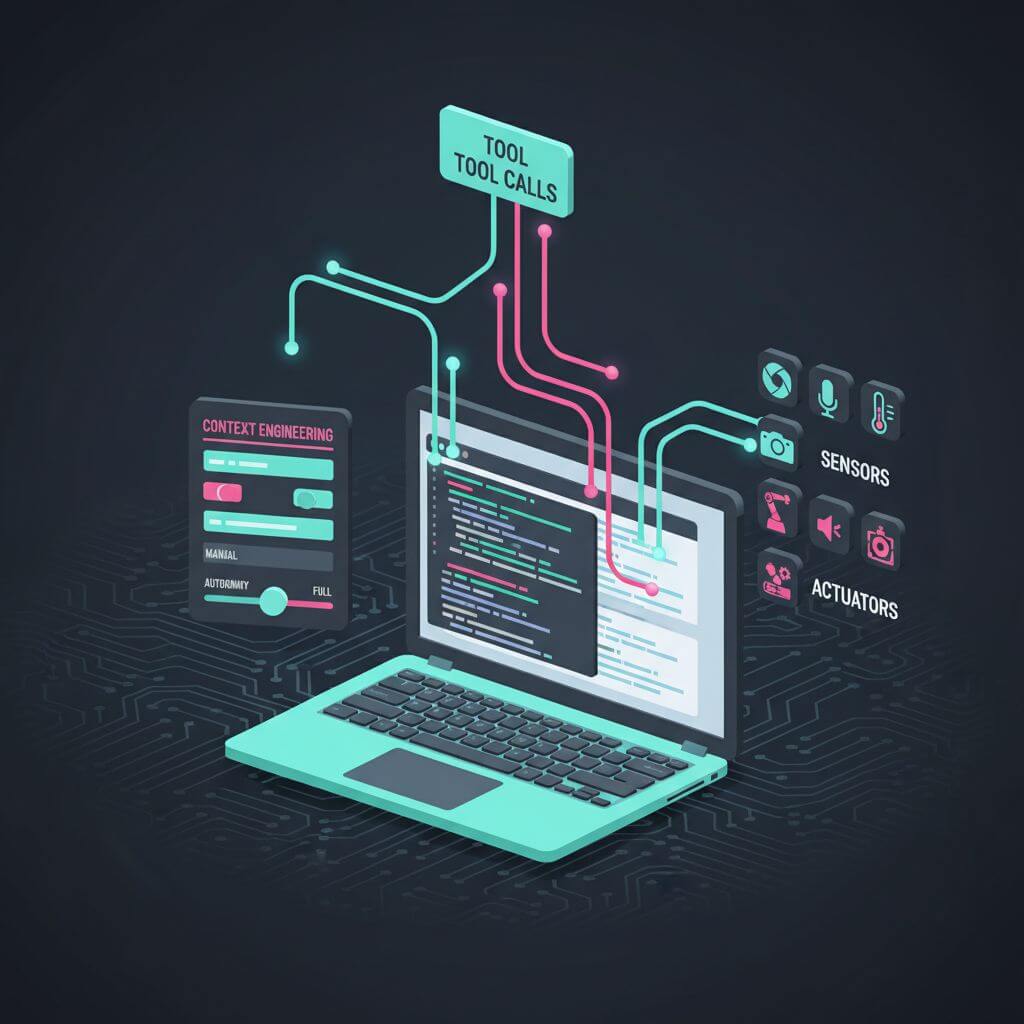
Cursor and the new layer of LLM apps
What an LLM app does
Cursor surged by bundling LLMs into a productized workflow for a vertical (coding):
- Context engineering that persistently frames the task
- Orchestrated multi-call DAGs balancing cost/latency/quality
- Human-in-the-loop GUI
- An “autonomy slider” exposing controllable agency
Verticalization vs. platform control
LLM labs will likely ship the “generally capable college student.” App builders will turn these students into domain professionals by adding private data, sensors/actuators, and feedback loops—organizational scaffolding that makes capability business-relevant.
Build tips
- Instrument everything; track token flows, errors, retries, tool efficacy.
- Cache aggressively; many verticals have high affordance for partial reuse.
- Design guardrails before autonomy: define reversible actions and escalation paths.

Claude Code: AI that lives on your computer
Cloud agent swarms feel like an endgame, but 2025 favored a slower, jagged-talent world where locality wins. Claude Code demonstrated a crisp pattern: agents running against your already-booted environment—your filesystem, secrets, config, and latency budget. The key isn’t where the compute happens; it’s where the context lives. A minimal CLI that wraps tools and reasoning loops reframed AI as a small spirit that inhabits your machine.
Vibe coding
Models crossed a threshold: you can build substantial software via English, often ignoring the underlying code. This empowers non-programmers, but it also unlocks a new kind of throughput for professionals—quick, disposable, single-purpose software to test ideas, isolate bugs, or scaffold systems. Code becomes free, ephemeral, and malleable, changing both the surface area of what gets built and the job descriptions that build it.
Practical patterns:
- Specify behavior, constraints, and tests; let the model fill in language/framework choices.
- Keep feedback tight: run-lint-fix cycles over long descriptive prompts.
- Treat generations as drafts; bake validation into the loop.
Nano banana and the LLM GUI
Chat is the command line of LLMs. People prefer visuals—diagrams, slides, whiteboards, small apps. Google’s Gemini Nano “banana” hinted at an LLM GUI layer: not just image output, but tightly coupled text+image generation grounded in world knowledge. Expect interfaces where models respond with structured visuals by default and tools that let users manipulate outputs spatially.
Design implications:
- Response modalities should match user cognition, not model convenience.
- Visual reasoning aids (timelines, graphs, schemas) should be first-class outputs.
- Joint multimodal weights matter more than piping text to separate image models.
FAQ
How is RLVR different from RLHF?
RLHF optimizes a learned preference model (subject to gaming); RLVR optimizes against objective, programmatically checkable rewards. That enables longer training and more reliable gains in verifiable domains.
Why are benchmarks less trustworthy now?
Because they’re verifiable, they’re easy to target. Labs can train close to them (or synthesize near-distribution data), inflating scores without robust generalization.
Should I run agents locally or in the cloud?
If your tasks rely on local context (repos, secrets, config) and need low latency, local-first often wins. Cloud is great for scale and isolation. Many teams do hybrid: local loop for context, cloud for heavy tools.
What does “thinking time” control in practice?
It governs trace length and search depth. More thinking time usually improves correctness on complex tasks—but costs tokens and may increase overfitting to spurious patterns without good evaluations.
Will vibe coding replace professional engineers?
It changes the surface area of work rather than eliminating it. Professionals orchestrate systems, validate behavior, design interfaces, and harden deployments—work that becomes more important as code generation scales.
Conclusion
2025 revealed LLMs as a new kind of intelligence: in some ways much smarter than expected, in others surprisingly brittle. RLVR, local agents, vertical apps, vibe coding, and multimodal GUIs expanded what’s possible—yet the frontier remains wide open. Expect rapid progress and plenty of engineering left to do. If you need to quickly convert a webpage to PDF or Markdown, you can try URL to Any.